Explaining, convincing and proving
-

-
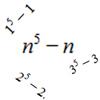 problem
problemCommon divisor
Find the largest integer which divides every member of the following sequence: 1^5-1, 2^5-2, 3^5-3, ... n^5-n. -
 problem
problemThree ways
If x + y = -1 find the largest value of xy by coordinate geometry, by calculus and by algebra. -
 problem
problemFitting in
The largest square which fits into a circle is ABCD and EFGH is a square with G and H on the line CD and E and F on the circumference of the circle. Show that AB = 5EF. Similarly the largest equilateral triangle which fits into a circle is LMN and PQR is an equilateral triangle with P and Q on the line LM and R on the circumference of the circle. Show that LM = 3PQ -
 problem
problemA biggy
Find the smallest positive integer N such that N/2 is a perfect cube, N/3 is a perfect fifth power and N/5 is a perfect seventh power. -
 problem
problemPair squares
The sum of any two of the numbers 2, 34 and 47 is a perfect square. Choose three square numbers and find sets of three integers with this property. Generalise to four integers. -
 problem
problemDiverging
Show that for natural numbers x and y if x/y > 1 then x/y>(x+1)/(y+1}>1. Hence prove that the product for i=1 to n of [(2i)/(2i-1)] tends to infinity as n tends to infinity. -
 problem
problemStaircase
Solving the equation x^3 = 3 is easy but what about solving equations with a 'staircase' of powers? -
 problem
problemKnight defeated
The knight's move on a chess board is 2 steps in one direction and one step in the other direction. Prove that a knight cannot visit every square on the board once and only (a tour) on a 2 by n board for any value of n. How many ways can a knight do this on a 3 by 4 board? -
 problem
problemLoopy
Investigate sequences given by $a_n = \frac{1+a_{n-1}}{a_{n-2}}$ for different choices of the first two terms. Make a conjecture about the behaviour of these sequences. Can you prove your conjecture?
