Music teachers challenge students to listen and participate.
English and History teachers invite students to journey in other
worlds.
Art and Drama teachers offer students opportunities to explore.
What are we to offer students if they are to function
mathematically?
What do you understand by 'functioning mathematically'?
What characteristic behaviours do your highly achieving
mathematicians exhibit?
Three key characteristics
- working systematically
- generalising
- proving and explaining
| Many
students |
Highly attaining students |
| work randomly |
work systematically |
| notice obvious patterns |
conjecture and generalise |
| make statements |
offer explanations and proofs |
What do these behaviours look like in practice?
Many numbers can be expressed as the sum of two or more
consecutive integers.
$15 = 7 + 8$
$15 = 4 + 5 + 6$
$15 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5$
Look at numbers other than 15 and find out all you can about
writing them as sums of consecutive whole numbers.
Working randomly:
$5=2+3$
$4+5+6+7=22$
$1+2+3+4+5+6=21$
$11=5+6$
Working systematically:
| $2$ |
$3$ |
$4$ |
| $1=0+1$ |
|
|
| $2=$ |
|
|
| $3=1+2$ |
$0+1+2$ |
|
| $4=$ |
|
|
| $5=2+3$ |
|
|
| $6=$ |
$1+2+3$ |
$0+1+2+3$ |
| $7=3+4$ |
|
|
| $8=$ |
|
|
| $9=4+5$ |
$2+3+4$ |
|
| $10=$ |
|
$1+2+3+4$ |
Noticing obvious patterns
- Odd numbers can be written as two consecutive numbers.
- Multiples of 3 can be written as three consecutive
numbers.
- Even numbers can be written as four consecutive
numbers.
Conjecturing and
generalising
- Multiples of 3 can be written as the sum of three
consecutive numbers.
- Multiples of 5 can be written as the sum of five
consecutive numbers.
- I wonder if multiples of 7 can be written as the sum of
seven consecutive numbers'?¦
- I wonder if multiples of 9 can be written as the sum of
nine consecutive numbers'?¦
- I wonder if multiples of x (where x is odd), can be written
as x consecutive numbers'?¦
Making statements
- Multiples of 3 can be written as three consecutive
numbers.
- If you give me any multiple of three, I can tell you the
three numbers by dividing by three and that will be the middle
number.
- Even numbers can be written as four consecutive
numbers.
Offering explanations and
proofs
- If you give me three consecutive numbers I can always turn
them into a multiple of three.
- x + (x+1) + (x+2) = (x+1) + (x+1) + (x+1) = 3 (x+1)
- Same will apply to five, seven, nine and any odd number
because you can pair off numbers on either side of the middle
number.
Creating opportunities for students to develop their
mathematical thinking
- Promoting a conjecturing atmosphere
- Careful use of questions and prompts
- Low threshold high ceiling tasks
- Modelling behaviour
- Whole class discussion
- Highlighting behaviour that you want to promote
- HOTS not MOTS
Promoting a conjecturing atmosphere
- Accepting 'messy' work
- Valuing risk-taking and half-formed ideas
- Encouraging discussion
- Providing thinking time
Careful use of questions and prompts
- What have you found out so far?
- Do you notice anything?
- Is that always true?
- Can you convince us?
- Can anyone think of a counter example?
- What if...?
- What might you try next?
- Is there a way you could organise your findings?
Low threshold high ceiling tasks
- Using problems that everyone can 'get into' but which also
offer opportunities for working at a higher level
- There is no need to 'label' students in advance
Modelling behaviour
Students should be in the presence of a teacher who is
- curious
- intrigued
- wanting to find out more
- appreciates the value of proof
- expects to understand why things happen
Whole class discussion
- Early on: to share
-
- Half way through: to share
-
- possible findings
- useful strategies
- new questions
- Towards the end: to share
-
- conclusions
- explanations
- proofs
Highlighting behaviour that you want to promote
Drawing
attention to and valuing process as well as outcome.
HOTS not MOTS
Higher Order Thinking Skills
not
More of the Same
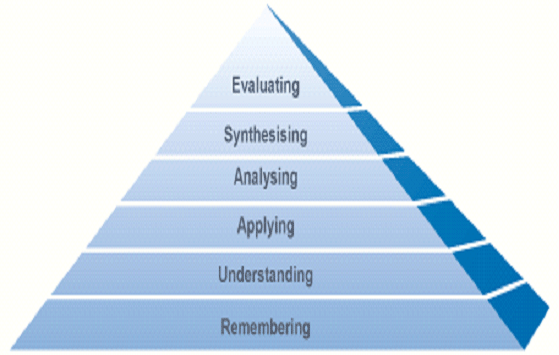
Each task requiring lower order thinking has a higher order
thinking equivalent/partner. Identify which is which and sort
them into pairs. (see Lower and Higher Order Thinking document)
How can you generate questions that promote these HOTS in a
mathematical context?
- Ask students to work backwards
- Ask "what if...?" questions
- Set questions which have a variety of solutions
- Set questions which can be solved in a variety of ways
Ask students
to work backwards
Instead of:
Find the area and perimeter of a 3cm x 8cm rectangle
ask:
If the area of a rectangle is 24cm² and the perimeter is
22cm, what are its dimensions?
Ask "what
if...?" questions
Instead of:
Find the area and perimeter of a 3cm x 8cm rectangle
ask:
What if the area of a rectangle (in cm²) is equal to the
perimeter (in cm), what could its dimensions be?
Set questions
which have a variety of solutions
Instead of:
Find the perimeter of a 3cm x 8cm rectangle
ask:
Find a rectangle which has unit sides and a perimeter of 100.
How many answers are there and how do you know you've got them
all?
Set
questions which can be solved in a variety of ways
Instead of:
Find the area and perimeter of a 3cm x 8cm rectangle
ask:
If the area of a rectangle is
24cm² and the perimeter is 22cm, what are its dimensions?
How did you work this out?
"A teacher of mathematics has a great opportunity. If he fills
his allotted time with drilling his students in routine
operations he kills their interest, hampers their intellectual
development, and misuses his opportunity. But if he challenges
the curiosity of his students by setting them problems
proportionate to their knowledge, and helps them to solve their
problems with stimulating questions, he may give them a taste
for, and some means of, independent thinking."
Polya, G. (1945) How to Solve
it
"I don't expect, and I don't want, all children to find
mathematics an engrossing study, or one that they want to
devote themselves to either in school or in their lives. Only a
few will find mathematics seductive enough to sustain a long
term engagement. But I would hope that all children could
experience at a few moments in their careers...the power and
excitement of mathematics...so that at the end of their formal
education they at least know what it is like and whether it is
an activity that has a place in their future."
David Wheeler
This article was originally
presented to the Council of Boards of School Education in India
Conference,"Addressing Core Issues and Concerns in Science and
Mathematics", in Rishikesh, India in April 2007.
