Andrei from Romania sent in a good
solution to this problem.
(1)(a) We have to show that $qq^{-1} = 1$: $$q^{-1} = ({1\over
\sqrt 2} + {1\over \sqrt 2}{\bf i}) ({1\over \sqrt 2} - {1\over
\sqrt 2}{\bf i}) = {1\over 2}(1 - {\bf i}^2) = 1$$ (b)Take $x =
ti$ to be any point on the x-axis. Then $qx = ({1\over \sqrt 2} +
{1\over \sqrt 2}{\bf i})t{\bf i} = {-1\over \sqrt 2} + {1\over
\sqrt 2}{\bf i})t = xq.$
We have shown that $qx = xq$ and so $qxq^{-1} = x$.
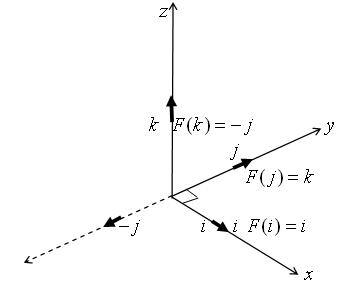 |
Let $F(v) = qvq^{-1}$ be a mapping of points $v$ in
$R^3$ to images in $R^3$ where the 4-dimensional quaternion
$q$ acts as an operator. We have proved that this mapping
fixes every point on the x axis. |
(c)What effect does this mapping have on other points in $R^3$?
$$F({\bf j})= qjq^{-1} = ({1\over \sqrt 2} + {1\over \sqrt
2}{\bf i})({\bf j}) ({1\over \sqrt 2} - {1\over \sqrt 2}{\bf
i})$$ $$ = {1\over 2}(1+{\bf i})({\bf j})((1 - {\bf i})$$ $$ =
{1\over 2}({\bf j} + {\bf k})(1 - {\bf i})$$ $$ = {1\over
2}({\bf j} + {\bf k} + {\bf k} - {\bf j})$$ $$= {\bf k}}.$$
Similarly $F{\bf k} = -{\bf j}$. Parts (b) and (c) together
show that the mapping $F(v) = qvq^{-1}$, where $q = \cos (\pi
/4) + \sin (\pi /4) {\bf i}$, gives a rotation of $\pi /2$
about the x axis.
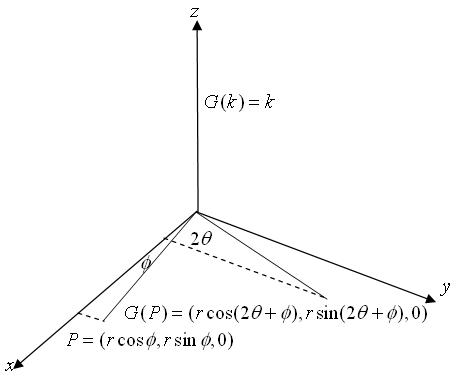 |
(2) In this section
we consider the mapping
of
to
where
the quaternion
is an operator.
|
(a)
so these two quaternions
are multiplicative inverses.
(b) We have
and hence
.
So the mapping
fixes the z-axis.
(c) What effect does the mapping
have on vectors in
?
We consider the vector
.
|
|
 |
We have shown
so
for all
.
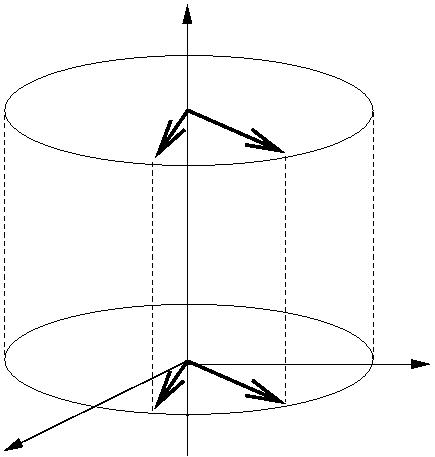
We can see that the vector
in the
plane is
rotated about the
axis by an angle
and all points on the
vertical line through it
are also rotated about
the
-axis by an angle
. So by the mapping
all points
in
are rotated by
about the
-axis.
Note that, for any rotation
of
, we can make a
transformation of the
coordinate system so that
the axis of the rotation
is made to coincide with the
-axis, then perform the
rotation by the given angle
about the
-axis, and
finally transform back to
the original coordinate
system.
|
