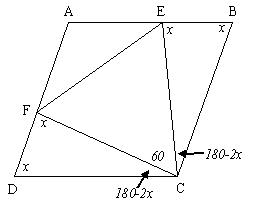
Triangle DFC is isosceles (CF=CD). Hence ÐDFC = ÐFDC = x°.
Hence ÐFCD = (180-2x)° (angle sum of triangle). Now ÐEBC = ÐFDC = x° (opposite angles of a parallelogram)
and triangle EBC is isosceles (CE = CB).
Hence ÐBEC = x° and ÐECB = (180-2x)°
Lines AD and BC are parallel and hence ÐADC + ÐBCD = 180°.
Therefore: x+2(180-2x) + 60 = 180 i.e.420-3x=180 i.e. 3x=240 i.e. x=80