Pythagoras (say "pie-thag-or-as") of Samos was a Greek
philosopher who lived from about 580 BC to about 500 BC. He made
important developments in mathematics, astronomy, and the theory
of music.
Pythagoras spent much of his life studying mathematics and
formed a special school where members followed strict rules, such
as never eating meat. Pythagoras believed that everything in the
world could be explained by numbers and his school worked hard to
try to learn enough about numbers to be able to understand the
universe.

This is
someone's idea of what Pythagorus might have looked like
Some of the things they believed about numbers seem odd to us
now. For example, numbers were thought to have their own special
nature. Pythagoreans thought numbers were male or female, ugly or
beautiful, or had a special meaning.
1 is the number of reason.
2 is the first even or female number, the number of
opinion.
3 is the first true male number, the number of
harmony.
4 is the number of justice or retribution.
5 means marriage.
6 is creation ...and so on.
Other ideas they worked on are
things you still learn about in school and that
mathematicians still use. Some of these are:
Odd numbers, like 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11
Even numbers, like 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12
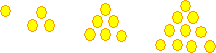
Triangular numbers, like 1, 3, 6, 10, 15
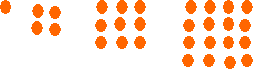
Square numbers, like 1, 4, 9, 16, 25
The school of Pythagoras also studied shapes and were
particularly interested in triangles. One theorem (a statement of
an idea) they worked on was:
The sum of the angles of a
triangle is equal to two right angles .
This means that if you take any triangle, tear off the corners
and fit them together like a puzzle, you will make a straight
line (that is the same as two right-angles).
Perhaps the most famous theorem in the world is known as
Pythagoras' theorem. It is thought that it was known to the
Babylonians 1000 years earlier but Pythagoras may have been the
first to prove it.
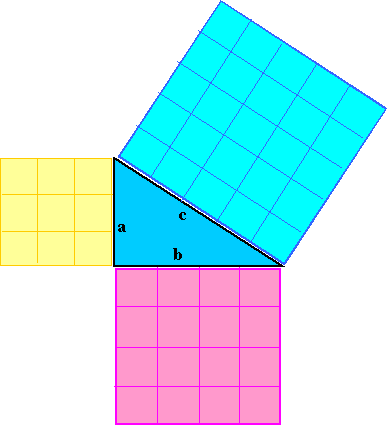
The theorem is: for a
right-angled triangle the square on the hypotenuse is equal to
the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
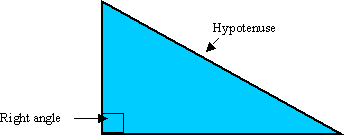
'Hypotenuse' is the name given to the side that is opposite the
right angle.
In this example, Side a is 3 cm long, so the area of the square on that side
is 3 x 3 = 9. Side b is 4 cm long, so the area of the square on that side is 4 x 4 = 16. Side c is 5 cm long, so the area of the square on that side is 5 x 5 = 25. Pythagoras' theorem says that if we add the smaller squares together we should
get the big square: 9 + 16 = 25 This can be written as can be written as a2 + b2 = c2
If you would like to find out more about Pythagoras visit the
St Andrews History of Mathematics website.