Correct solutions were received from Roy
of Allerton High School, Hannah of St Helen's and St Katharines
and Andre of Tudor Vianu National College, Bucharest. All used
the method below. Well done to you all.
The areas are equal.
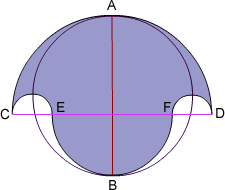
The salinon is composed of semicircles on CD, EF, CE and FD. Now we can find
the area of the salinon in terms of these semicircles as follows;
Let the big semicircle on CD have a radius of
, the medium one on EF be
radius
. Then the small circles on CE and FD have a radius of
and the circle on AB has radius
The area of the semicircle on CD is
The bottom semi circle (on EF) has an area of
The two smaller semi circles, on CE and FD together make a circle whose area
is
the total area of the salinon is: the top semi circle + the bottom semi
circle - the two smaller identical semi circles
or
multiplying out all the brackets you get
now for the area of the main circle with diameter AB:
the radius of the circle is
so the area of it is
which, when multiplied out is the same as the area of the salinon.
