In this problem we shall use arrows to describe how to get from
one point to another.
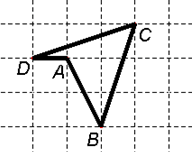
E.g.: In the diagram below we shall describe the journey from A
to B to C to D and back to A as follows:
|
A ® + ¯ ¯ B ® + C ¬ ¬ ¬ + ¯ D ® A |
|
A tilted square is a square with no horizontal sides.
For example, a square with vertices at (10,10), (17,13), (14,20)
and (7,17) is a tilted square.
Full
Screen Version
This text is usually replaced by the Flash movie.
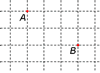
If AB is described as
A ® ® ® + ¯ ¯ B or A 3 ® + 2 ¯ B
| draw at least one square ABCD for which AB is a
side. |
 |
Draw squares ABCD for which one side is given below:
a) A 1 ® + 1 B b) A 2 ® + 1 B c) A 3 ® + 1 B d) A 2 ® + 2 B e) A 3 ® + 2 B
Complete the arrow notation for the squares ABCD. What do you
notice?
Formulate and describe a general instruction for the construction
of a square when you are given one of its sides.
Using the rule you developed above, decide whether any of the
collections of points below form a square.
If so, which ones?
1. (8,3), (7,8), (2,7), (3,2)
2. (3,3), (7,4), (8,8), (4,7)
3. (16,19), (18,22), (21,20), (19,17)
4. (4,20), (21,19), (20,2), (3,3)
Explain how you decided.


