Copyright © University of Cambridge. All rights reserved.
'Why Multiply When You're about to Divide?' printed from https://nrich.maths.org/
Show menu
The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify the amount of DNA in a sample. During each round of PCR, the DNA double helix is unwound and separated into two separate strands. A new strand is then synthesised against each of these.
How does the DNA content of a sample change with a single round of PCR?
If there is originally 1mg of DNA in the sample, then what mass of DNA will be present after 15 rounds of PCR?
If my sample of 0.5ml with a DNA concentration of 0.1pM, how many rounds of PCR until I have 10$^{12}$ molecules of DNA?
DNA synthesis in PCR is carried out by a Taq DNA polymerase. This can build a new strand of DNA against a template one at a rate of 6000 bases per minute.
If a piece of single stranded DNA has 24 kbases, what is the minimum number of minutes that should be left between rounds of PCR?
If I start with a single 24000 base pair DNA helix, and carry out 10 rounds of PCR, how many bases will have been incorporated into DNA at the end?
What is the point of PCR? Amplification of small quantities of DNA allows it to be analysed using a variety of methods -one of these techniques is restriction mapping. Restriction mapping relies on bacterially-derived restriction enzymes which can cut DNA at specific sequences. Each type of restriction enzyme cuts the DNA at a different but specific sequence. When a DNA helix has been cut using
these enzymes, the lengths of the fragments can be determined by using gel electrophoresis, which separates the molecules on the basis of size. By using different combinations of restriction enzymes to generate different length fragments, a map can be drawn of the original DNA with the location of each type of restriction site.
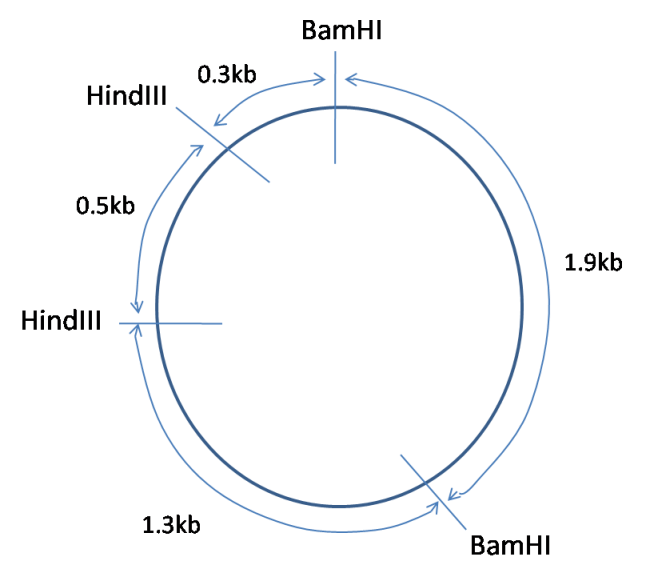
For example, a certain bacterial plasmid (circular DNA molecule) is digested with different combinations of restriction enzymes, and gives the following size fragments:
BamHI: 2.1kb, 1.9kb
HindIII: 3.5kb, 0.5kb
BamHI + HindIII: 1.9kb, 1.3kb, 0.5kb, 0.3kb.
From this data, is it possible to deduce the following map of the plasmid:
Using the above example as a guide, create a map of the restriction sites on the plasmid from the following data (all fragment lengths in kb):
