Matching Frieze Patterns
Problem
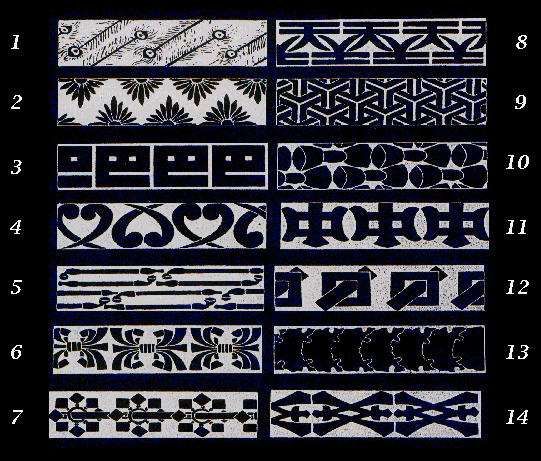
Each frieze pattern is formed by repeating copies of one small bit of the pattern (the motif) over and over again by translation, rotation and reflection. Sort the frieze patterns into seven pairs according to the way in which the motif is repeated. Explain how you match the pairs.
Image
|
Getting Started
Look for reflections in the axis along the strip and perpendicular to the strip.
Take care to distinguish glide reflections such as p b from rotations such as p d.
Student Solutions
The simplest patterns are 3 and 12 in which the motif is repeated by a translation along the strip. Translations are the only transformations involved. (p p p p p p p)
In patterns 1 and 5 the motif is rotated and then the motif (with this copy) is repeated by a translation. This pattern involves half turns and translations. (p d p d p d p d)
In patterns 7 and 13 there is a reflection in the horizontal axis and then the motif (with this copy) is repeated by a translation. This pattern involves reflections in the horizontal axis and translations. (E E E E E E)
In patterns 4 and 10 the first copy is made by a reflection in the horizontal axis combined with a translation (a glide reflection) and then the motif (with this copy) is repeated by a translation. This pattern involves glide reflections in the horizontal axis and translations. (p b p b p b p b p b)
In patterns 9 and 11 the first copy is made by a reflection in a mirror line perpendicular to the strip and then the motif (with this copy) is repeated by a translation. This pattern involves reflections in a perpendicular axis and translations. (b d b d b d b d b d)
In patterns 6 and 14 the motif is repeated by a combination of two reflections in the horizontal and perpendicular axes and then the motif (with this copy) is repeated by a translation. This pattern involves reflections in the horizontal and in a perpendicular axis, half turns and translations. (H H H H H H H H)
In patterns 2 and 8 the motif is repeated by a combination of a reflections in a perpendicular axis and a glide reflection and then the motif (with this copy) is repeated by a translation. This pattern involves reflections in a perpendicular axis, glide reflections, half turns and translations. (pqbd pqbd pqbd pqbd)
Teachers' Resources
These patterns are Japanese, but frieze patterns occur in many cultures. The article Frieze Patterns in Cast Iron also illustrates all seven types of frieze patterns.
See the article The Frieze Tree for a discussion of why there are only seven possible types of frieze pattern.
