Copyright © University of Cambridge. All rights reserved.
'Triangular Teaser' printed from https://nrich.maths.org/
Show menu
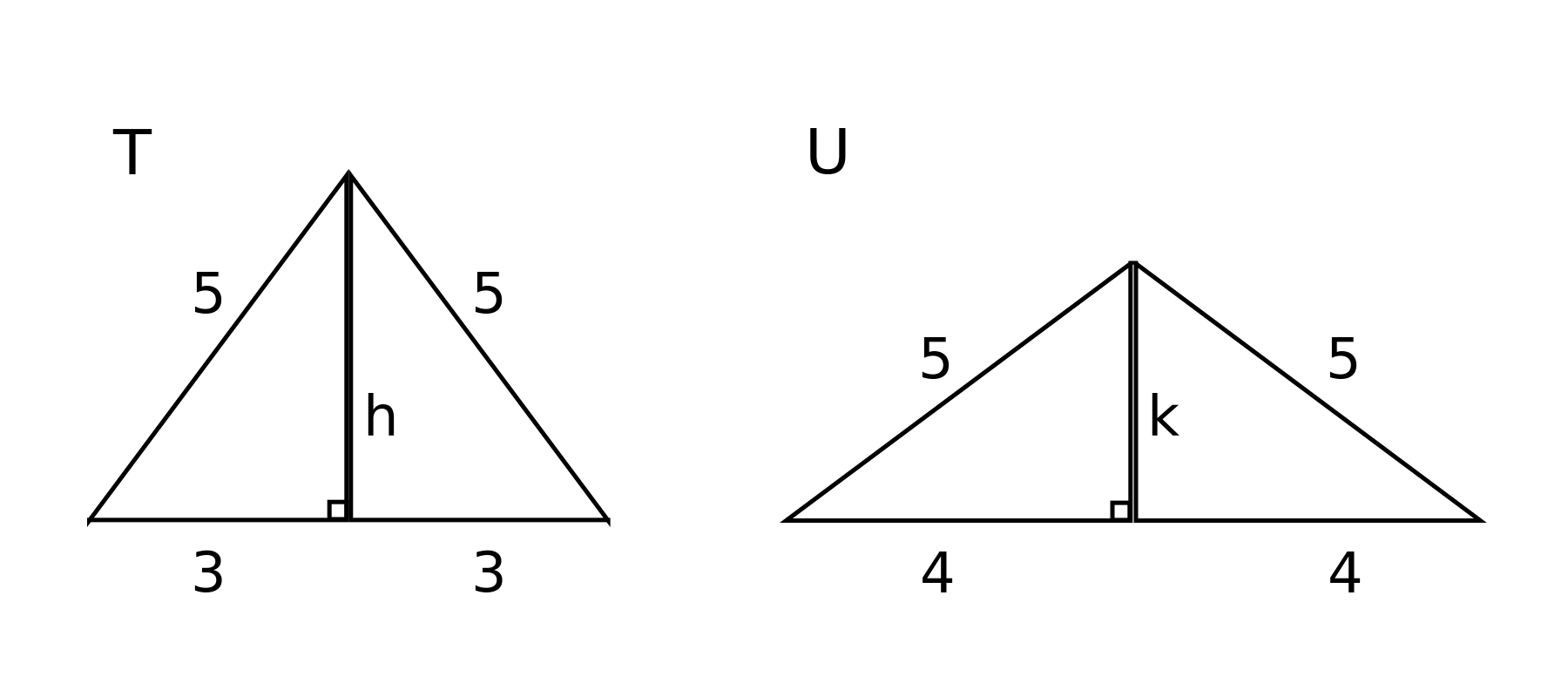
The diagram below shows isosceles triangles $T$ and $U$. The perpendicular from the top vertex to the base divides an isosceles triangle into two congruent right-angled triangles as shown in both $T$ and $U$. Evidently, by Pythagoras' Theorem, $h = 4$ and $k = 3$. So both triangles $T$ and $U$ consist of two $3$, $4$, $5$ triangles and therefore have equal areas.
This problem is taken from the UKMT Mathematical Challenges.
You can find more short problems, arranged by curriculum topic, in our short problems collection.