Copyright © University of Cambridge. All rights reserved.
'Extended Parallelogram' printed from https://nrich.maths.org/
Show menu
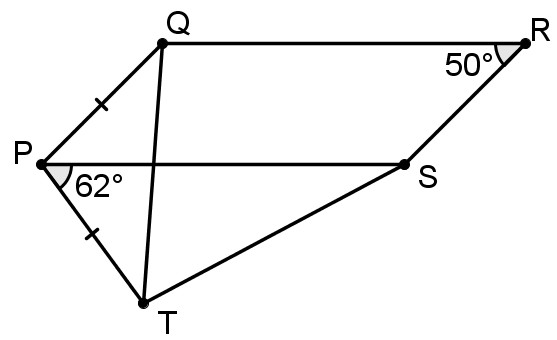
Opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal, so ∠QPS = 50 °. Therefore, ∠QPT = 112 ° and, as triangle QPT is isosceles, ∠PQT = (180 °-112 °)/2=34 °. As PQRS is a parallelogram, ∠PQR = 180 ° - 50 ° = 130 °.
So ∠TQR = 130 ° - 34 ° = 96 °.
This problem is taken from the UKMT Mathematical Challenges.
You can find more short problems, arranged by curriculum topic, in our short problems collection.